Chlorophylls and accessory pigments
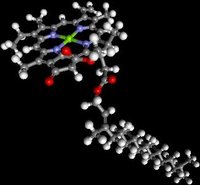
 A space-fill model of chlorophyll a (left), and a ball and stick model of chlorophyll a (right). A magnesium ion (green) lies at the centre of the ring structure)
A space-fill model of chlorophyll a (left), and a ball and stick model of chlorophyll a (right). A magnesium ion (green) lies at the centre of the ring structure) grey - carbon / white - hydrogen / blue - nitrogen / red - oxygen / green - magnesium
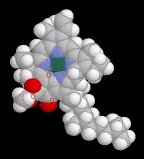
 The porphyrin ring is a complex of four heterocyclic pyrrole rings, which chelates Mg (green area in ball and stick model at left). The electron cloud associated with the porphyrin ring is available to harness incident light.
The porphyrin ring is a complex of four heterocyclic pyrrole rings, which chelates Mg (green area in ball and stick model at left). The electron cloud associated with the porphyrin ring is available to harness incident light. .. Chime animation of Chlorophyll a spinning
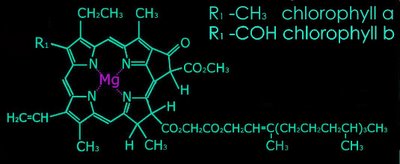
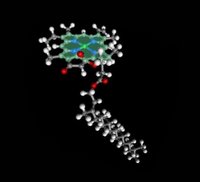
A phytol side chain is attached to the porphyrin ring. This side chain anchors the molecule into the photosynthetic thylakoid membrane. Chlorophylls a and b differ only in the character of the R1 group attached to the Mg-porphyrin ring moiety of the molecule: -CH3 for chlorophyll a, and -COH for chlorophyll b. Bacteriochlorophylls possess different side chains and different groups attached to the porphyrin rings.
Chlorophyll a: green plants, algae, Cyanobacteria.
Chlorophyll b: green algae, plants
Chlorophyll b: dinoflagellates, photosynthetic Chromista
The overall reaction of photosynthesis is:
6H2O + 6CO2 --> C6H12O6+ 6O2
Although the reaction formula is simple, reaction mechanics of photosynthesis are complex.

A phytol side chain is attached to the porphyrin ring. This side chain anchors the molecule into the photosynthetic thylakoid membrane. Chlorophylls a and b differ only in the character of the R1 group attached to the Mg-porphyrin ring moiety of the molecule: -CH3 for chlorophyll a, and -COH for chlorophyll b. Bacteriochlorophylls possess different side chains and different groups attached to the porphyrin rings.
Chlorophyll a: green plants, algae, Cyanobacteria.
Chlorophyll b: green algae, plants
Chlorophyll b: dinoflagellates, photosynthetic Chromista
The overall reaction of photosynthesis is:
6H2O + 6CO2 --> C6H12O6+ 6O2
Although the reaction formula is simple, reaction mechanics of photosynthesis are complex.
See also: Structure and Reactions of Chlorophyll External link Chlorophylls and accessory pigments
HOME • • Section Photosynthesis • Calvin cycle • C-3 • C-4 • CAM • Chloroplast • Chlorosomes • Cyanobacterial cell : cyclic photophosphorylation : • Light-reactions : noncyclic photophosphorylation : • Nonoxygenic photosynthesis • Oxygenic photosynthesis • Photosynthesis Overview • Photophosphorylation • Plant cell • Timeline • • Section Pigments • Antenna and Reaction Center • Bacteriochlorophylls • Carotenoids • Chlorophylls and accessory pigments • Pigments and absorption spectra • Phycobilins Section Articles • SITE MAP •








































1 Glossary:
Absorption Spectrum: results from the ability of pigments to absorb incident electromagnetic radiation. Like the action spectrum, the parameter of interest (light absorbed) is plotted as a function of the wavelength of the radiation. This is the opposite of an emission spectrum where wavelengths emitted by a substance are measured.
Action Spectrum: the efficiency of photochemical response to incident electromagnetic radiation. Like the absorption spectrum, the parameter of interest (here photochemical reaction) is plotted as a function of the wavelength of the radiation.
The action spectrum of photosynthesis within an organism resembles the absorption spectra of chlorophyll though it is not identical. This difference arises because accessory pigments play a part in photosynthetic efficiency.
<< Home